
 Flash News
Flash News
Behind the scenes of a fake article, BIRN journalist: Anonymous authors to influence public opinion
Accident in Lushnje, four cars and a motorcycle involved
SPAK closed the investigations, Meta reacts: It was signed on the orders of Edi Rama
Defendant was taken from SPAK, Kryemadhi: Chief Prosecutor of BKH is Edi Rama
Laundered Çopjave money, arrested in Dubai Armis Stafa
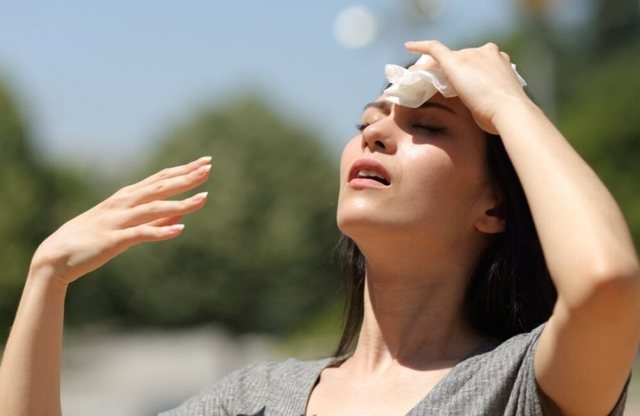

The side effects of heat on health are manifested when the internal temperature regulation system fails to eliminate the excess amount of heat in order to maintain normal body temperature values.
Prolonged periods with extreme meteorological conditions, characterized by the increase of temperatures above the usual values, impose the undertaking of some measures for the prevention and treatment of the side effects of heat on health.
The side effects of heat on health are manifested when the internal temperature regulation system fails to eliminate the excess amount of heat in order to maintain normal body temperature values. Deficits in compensation initially manifest with signs and symptoms easily correctable with cessation of heat exposure.
But if exposure continues, the signs and symptoms of decompensation become more serious and are known as heat stress and heatstroke.
Extreme temperature increases can aggravate the condition of people with chronic pathologies. The main way of eliminating heat is through sweating, but in extreme physical and environmental situations, this mechanism is insufficient. If the degree of humidity in the environment is high, the sweat evaporates slowly and the body temperature can reach values above 40°C, damaging the vital organs of the organism.
Factors affecting thermoregulation are:
1. Age (in young children and the elderly it is reduced)
2. Pre-existing diseases
3. Use of certain medications
4. Drug and alcohol consumption
Signs and symptoms of heatstroke:
The first to appear are:
1. Headache;
2. Nausea and vomiting;
3. Pale and warm skin;
4. Weak pulse;
5. Increase in body temperature;
6. State of being inactive;
7. Edema;
8. Muscle cramps;
If exposure continues:
9. Disorders of consciousness ranging from confusion to complete loss of consciousness;
10. Convulsions;
10. Increased heart rate;
11. Severe cerebral damage, acute cardiac decompensation and death.
Protocol of measures for the prevention of heat injuries
1. Avoid exposure to the sun. Especially at peak temperatures (from 11:00 a.m. to 5:00 p.m.)
2. The environment in which they live should be fresh and well ventilated, through air conditioning, fans or nebulizers for humidifying the air. Place dark curtains, especially on windows exposed to solar radiation. Place thermometers to measure the temperature of the environment where they spend most of their time.
3. Drink as much liquid as possible, mainly water. Avoid very cold drinks, carbonated drinks, with a lot of sugar and other additives.
4. Consume frequent food meals, in small quantities, cold and with easily digestible food ingredients.
5. To wear light clothes, with light colors and made of cotton or linen in order to break the UV radiation.
6. For people who use maintenance therapy, do not stop or change it, without consulting the relevant doctor.
7. Frequent showers with lukewarm water and without drying with a towel are recommended.
Latest news







70 Albanians from Kosovo and Albania are deported from Germany
2025-05-27 20:59:16


Italy/ 39-year-old Albanian man crashes to death while waiting to go to work
2025-05-27 20:15:03
SPAK's accusations against Meta, AP: Former president openly critical of Rama
2025-05-27 20:09:47
Accident in Lushnje, four cars and a motorcycle involved
2025-05-27 19:44:24


Rama eating pasta, photojournalist reveals the story behind the viral photo
2025-05-27 19:13:56
Meat with salmonella still on the market? AKU reacts: Fake news
2025-05-27 19:03:29
Violations of May 11, Lela: 'Database' ready, internationals are being informed
2025-05-27 18:47:40
Scandal with animal products in Kosovo, Minister of Agriculture questioned
2025-05-27 18:47:24
Congratulations... to the Albanian people
2025-05-27 18:20:00

"SP stole 2 mandates from us", Lapaj: Fier and Vlora regions must be recounted
2025-05-27 17:42:39

Kosovo takes control of another facility in Leposavic
2025-05-27 17:25:55



DP demands repeat elections in Gjirokastra and Vlora
2025-05-27 16:37:47
Should Berisha resign? Alimehmeti: Stages cannot be burned
2025-05-27 16:18:22


Sunscreen, five myths that endanger your health
2025-05-27 15:52:57

EC chief condemns Israeli attacks on Gaza: They are disgusting
2025-05-27 15:23:30



Defendant was taken from SPAK, Kryemadhi: Chief Prosecutor of BKH is Edi Rama
2025-05-27 14:47:32

Police raid Kosovo's Ministry of Agriculture
2025-05-27 14:31:07
Laundered Çopjave money, arrested in Dubai Armis Stafa
2025-05-27 14:22:55
Tried to kill cousin in Italy? Case against Albanian from Kosovo closed
2025-05-27 14:12:33



Prostitution network busted, Brazilian woman declared wanted
2025-05-27 13:31:20

SPAK took the defendant, Meta reacts: I eagerly await the start of the trial
2025-05-27 13:11:06

A party with a dead body inside
2025-05-27 12:51:40





Session to constitute Kosovo Assembly fails for the 22nd time
2025-05-27 11:53:33
He passed away a few days ago, tributes are being held in honor of Artan Lame
2025-05-27 11:44:47
Reactions to Macron's slap
2025-05-27 11:32:35

Greek notary killed with intent to rob her, 3 Albanians arrested
2025-05-27 11:11:25
Aulona Kalaja appears at SPAK, files a complaint for the forgiveness of fines
2025-05-27 10:58:24

Meta will use Europeans' posts for AI training
2025-05-27 10:42:07

The Democratic Party appeals the election results in Korça
2025-05-27 10:23:11

Igli Tare appointed Milan Sporting Director
2025-05-27 10:03:54
Albanian caught with cocaine worth around 14 million euros
2025-05-27 10:00:56

Foreign exchange/ How much foreign currencies are bought and sold today
2025-05-27 09:40:13

Brussels presents 150 billion euro plan to strengthen EU defense capabilities
2025-05-27 09:14:33

He raped his minor daughter, 60-year-old man arrested (NAME)
2025-05-27 08:57:54


Artan Lame is being transported to his final residence today
2025-05-27 08:26:24
Horoscope, what do the stars have in store for you today?
2025-05-27 08:15:43
Weather forecast, sun and temperatures up to 29 degrees during the day
2025-05-27 08:01:32
Morning Post/ In 2 lines: What mattered yesterday in Albania
2025-05-27 07:47:24





WHO calls for medical aid trucks to be allowed into Gaza
2025-05-26 21:46:31
Did he want to burn it by running in Vlora? Gjiknuri: Rama experimented
2025-05-26 21:39:25


REL: Serbian police order for the arrest of Kosovo policeman, "very unreal"
2025-05-26 21:01:48


Milan officially announces the appointment of Igli Tara as Sporting Director
2025-05-26 19:43:14

Former Kosovo MP released after being detained at border by Serbian authorities
2025-05-26 19:24:50
Magnificent buffet in Hanoi
2025-05-26 19:03:41


