
 Flash News
Flash News
Gunfire in Durres, a 30-year-old man is injured
Accident on Arbri Street, car goes off the road, two injured
Arrests of "Bankers Petrolium", Prosecution provides details: Exported and sold 532 billion lek of oil, caused millions of euros in damage to the state
Ndahet nga jeta tragjikisht në moshën 28-vjeçare ylli i Liverpool, Diogo Jota
Posta e mëngjesit/ Me 2 rreshta: Çfarë pati rëndësi dje në Shqipëri

Botox, or botulinum toxin, is a drug that is produced from a bacterial toxin, and is usually injected into the human body to reduce wrinkles, relieve pain caused by migraines, muscle spasms, excessive sweating and urinary incontinence.
But researchers at the University of California School of Pharmacy and Pharmaceutical Sciences, in collaboration with 2 doctors from Germany, may have discovered a new use for it thanks to the US Food and Drug Administration's Adverse Effect Reporting System (FAERS). FDA), where nearly 40,000 people reported what happened to them after Botox treatment for a variety of reasons.
The study, published on December 21, 2021 in the journal "Scientific Reports", found that people who received Botox injections in 4 different areas of the body - so not just the forehead - reported significantly less anxiety episodes than patients who underwent different treatments for the same conditions.
“A large number of different adverse effects have been reported to the FDA. And the main objective is usually to find those harmful side effects that were not identified during clinical trials. But our idea was different. We said: Why not do the opposite? Why not find the beneficial effects?" - says Robert Abagian, professor of pharmaceuticals.
Abagian and his team searched the database for information on the absence or reduced frequency of anxiety and related disorders, with anxiety as a health complaint, compared to a control group, when respondents received Botox.
The team then used a mathematical algorithm to find statistically significant differences between Botox users and patients who received different treatments.
for the same conditions. What they found was that the reported risk of anxiety was 22-72 percent lower in patients treated with Botox for 4 of 8 conditions and injection sites: facial muscles for cosmetic use; facial and head muscles for migraine treatment; upper and lower limbs for spasms and spasticity; and neck muscles for torticollis.
According to the National Comorbidity Survey Replication, a study of the prevalence and correlates of mental disorders in the US, conducted between 2001 and 2003, anxiety disorders are the most common category of psychiatric disorders.
Sipas sondazhit, 32 për qind e popullsisë amerikane ndikohen negativisht nga ankthi në një moment të jetës së tyre, dhe trajtimet janë joefektive për gati 1/3 e tyre. Kjo është arsyeja pse klinicistët dhe studiuesit po kërkojnë opsione të tjera terapeutike.
Sigurisht, të dhënat e përdorura në këtë studim nuk u mblodhën me synimin ekskluziv të zbulimit të një lidhje midis përdorimit të botoks dhe ankthit. Për më tepër, të dhënat e FAERS përfaqësojnë vetëm nëngrupin e përdoruesve të botoksit, që përjetuan efekte anësore negative.
Ndërkohë Abagian dhe ekipi i tij, publikuan një studim të ngjashëm po në“Scientific Reports” në korrikun e vitit 2020, në të cilin, duke përdorur të njëjtën bazë të dhënash, zbuluan se njerëzit që morën injeksione me botoks raportuan dukshëm më rrallë gjendje depresive sesa pacientët që i nënshtroheshin trajtimeve të ndryshme për të njëjtat kushte.
Abagian dhe bashkëpunëtorët e tij thonë se duhen analizuar disa mekanizma të mundshëm, që mund të shpjegojnë lidhjen. Toksinat botulinum mund të transportohen në rajonet e sistemeve nervore qendrore, që janë përgjegjëse për humorin dhe emocione.
The neuromuscular junctions affected by botox can communicate directly with the brain. Finally, since Botox is commonly used to treat chronic conditions that may contribute to anxiety, its success in alleviating the underlying problem may also indirectly ease the anxiety symptoms themselves.
Latest news










Greece imposes fee to visit Santorini, how many euros tourists must pay
2025-07-03 20:50:37
Don't make fun of the highlanders, Elisa!
2025-07-03 20:43:43
Gunfire in Durres, a 30-year-old man is injured
2025-07-03 20:30:52

The recount in Fier cast doubt on the integrity of the vote
2025-07-03 20:09:03




Heatwave has left at least 9 dead this week in Europe
2025-07-03 19:00:01

Oil exploitation, Bankers accused of 20-year fraud scheme
2025-07-03 18:33:52
Three drinks that make you sweat less in the summer
2025-07-03 18:19:35
What we know so far about the deaths of Diogo Jota and his brother André Silva
2025-07-03 18:01:56



Another heat wave is expected to grip Europe
2025-07-03 17:10:58

Accident on Arbri Street, car goes off the road, two injured
2025-07-03 16:45:27

Accused of two murders, England says "NO" to Ilirjan Zeqaj's extradition
2025-07-03 16:25:05





Gaza rescue teams: Israeli forces killed 25 people, 12 in shelters
2025-07-03 15:08:43
Diddy's trial ends, producer denied bail
2025-07-03 15:02:41

Agricultural production costs are rising rapidly, 4.8% in 2024
2025-07-03 14:55:13
Warning signs of poor blood circulation
2025-07-03 14:49:47
Croatia recommends its citizens not to travel to Serbia
2025-07-03 14:31:19
Berisha: Albania is the blackest stain in Europe for the export of emigrants
2025-07-03 14:20:19


'Ministry of Smoke': Activists Blame Government for Wasteland Fires
2025-07-03 13:59:09

AFF message of condolences for the tragic loss of Diogo Jota and his brother
2025-07-03 13:41:36
Five healthy foods you should add to your diet
2025-07-03 13:30:19






A unique summer season, full of rhythm and rewards for Credins bank customers!
2025-07-03 12:12:20

Fire situation in the country, 29 fires reported in 24 hours
2025-07-03 12:00:04
The constitution of the Kosovo Assembly fails for the 41st time
2025-07-03 11:59:57
The gendering of politics
2025-07-03 11:48:36
The price we pay after the "elections"
2025-07-03 11:25:39

Xhafa: The fire at the Elbasan landfill was deliberately lit to destroy evidence
2025-07-03 11:08:43

The 3 zodiac signs that will have financial growth during July
2025-07-03 10:48:01
Democratic MP talks about the incinerator, Spiropali turns off her microphone
2025-07-03 10:39:24

Ndahet nga jeta tragjikisht në moshën 28-vjeçare ylli i Liverpool, Diogo Jota
2025-07-03 10:21:03
Cocaine trafficking network in Greece, including Albanians, uncovered
2025-07-03 10:10:12



Korreshi: Election manipulation began long before the voting date
2025-07-03 09:39:13
Arrest of Greek customs officer 'paralyzes' vehicle traffic at Qafë Botë
2025-07-03 09:28:41
After Tirana and Fier, the boxes are opened in Durrës today
2025-07-03 09:21:10
Enea Mihaj transfers to the USA, will play as an opponent of Messi and Uzun
2025-07-03 09:10:04

Foreign exchange, the rate at which foreign currencies are sold and bought
2025-07-03 08:53:50
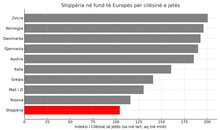
Index, Albania has the worst quality of life in Europe
2025-07-03 08:48:10


Horoscope, what do the stars have in store for you today?
2025-07-03 08:17:05
Clear weather and high temperatures, here's the forecast for this Thursday
2025-07-03 08:00:37
Posta e mëngjesit/ Me 2 rreshta: Çfarë pati rëndësi dje në Shqipëri
2025-07-03 07:46:48



Lufta në Gaza/ Pse Netanyahu do vetëm një armëpushim 60-ditor, jo të përhershëm?
2025-07-02 21:56:08
US suspends some military aid to Ukraine
2025-07-02 21:40:55



Methadone shortage, users return to heroin: We steal to buy it
2025-07-02 20:57:35
Government enters oil market, Rama: New price for consumers
2025-07-02 20:43:30
WHO calls for 50% price hike for tobacco, alcohol and sugary drinks
2025-07-02 20:41:53



